Project title: JAIST Gallery
Completion: 2012
Location: JAIST (Japan Advanced Institute of Science And Technology), 1-1, Asahidai, Nomi-city, Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan
Design: Tatsu Matsuda / Tatsu Matsuda Architects, Noriko Rinno / Rinno Architecutal office, Japan
Site surveillance cooperation: Toshihiro Yoshimura / Toshihiro Yoshimura Architect
Structural engineering Adviser: Yasutaka Konishi / Konishi Structural Engineers
Lighting design: Mariko Naito / Komorebi Design
Equipment planner: Tadashi Nakamura Equipment Planning
Construction: Yamamori Kogyo Co.
Electric works: Shiguma Electric Co.
HVAC: Suzuki Kensho Co.
Furniture design: CELIA s.p.A.
Construction type: Expansion
Period of construction: July 2012-September 2012
Construction structure: Existing Reinforced Concrete Construction with seven stories
Built surface: 157.74 m2
Total floor area: 157.74 m2
Related information: JAIST Gallery's web site
Completion: 2012
Location: JAIST (Japan Advanced Institute of Science And Technology), 1-1, Asahidai, Nomi-city, Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan
Design: Tatsu Matsuda / Tatsu Matsuda Architects, Noriko Rinno / Rinno Architecutal office, Japan
Site surveillance cooperation: Toshihiro Yoshimura / Toshihiro Yoshimura Architect
Structural engineering Adviser: Yasutaka Konishi / Konishi Structural Engineers
Lighting design: Mariko Naito / Komorebi Design
Equipment planner: Tadashi Nakamura Equipment Planning
Construction: Yamamori Kogyo Co.
Electric works: Shiguma Electric Co.
HVAC: Suzuki Kensho Co.
Furniture design: CELIA s.p.A.
Construction type: Expansion
Period of construction: July 2012-September 2012
Construction structure: Existing Reinforced Concrete Construction with seven stories
Built surface: 157.74 m2
Total floor area: 157.74 m2
Related information: JAIST Gallery's web site
Photo: Hiraku Ikeda
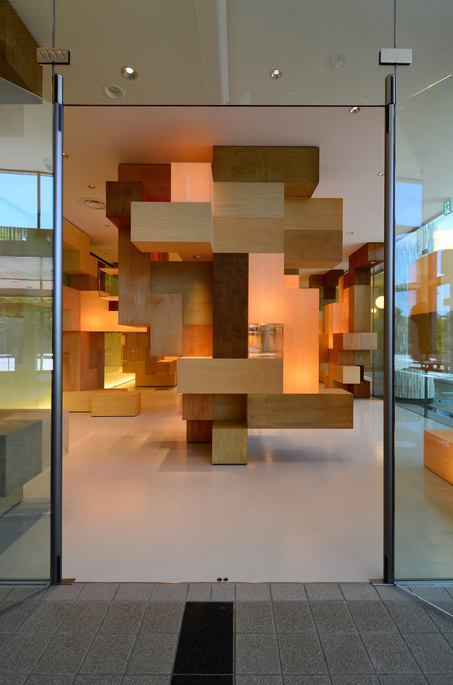
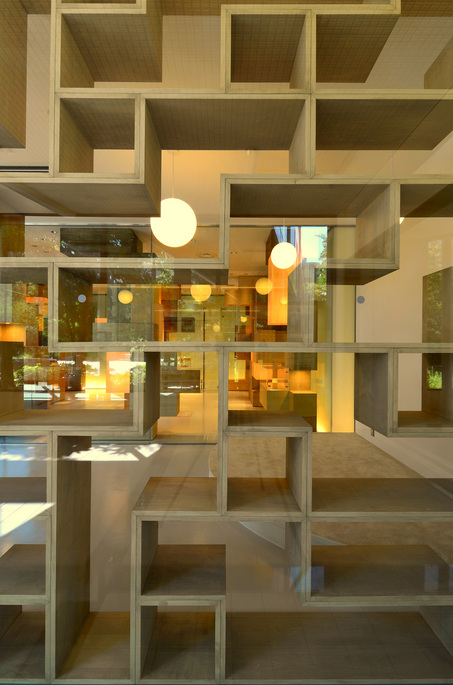
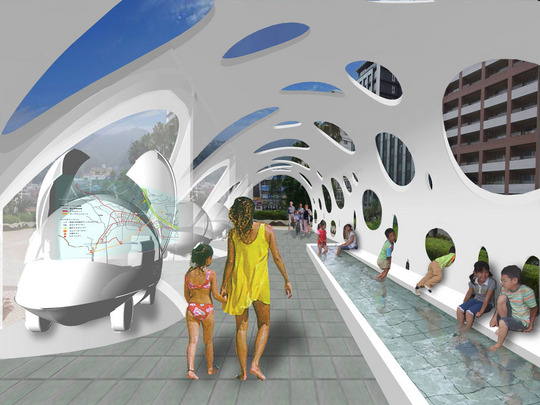
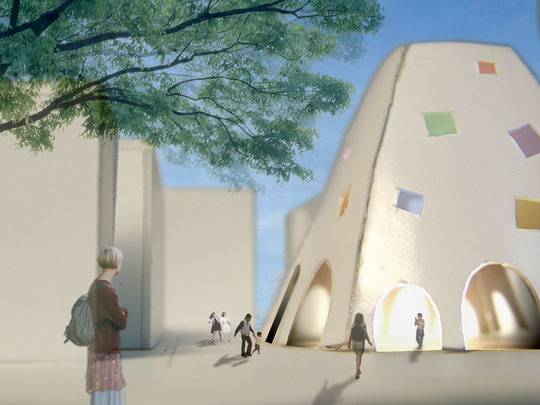
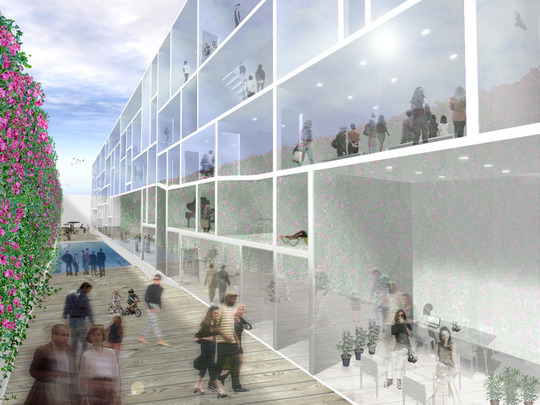
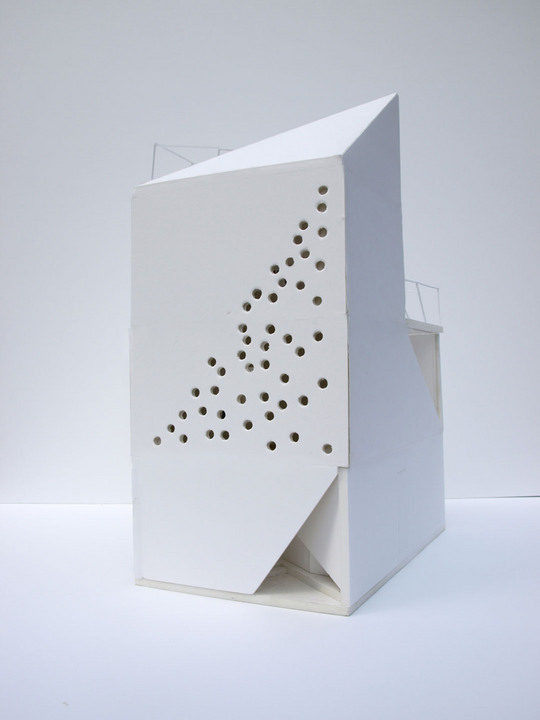
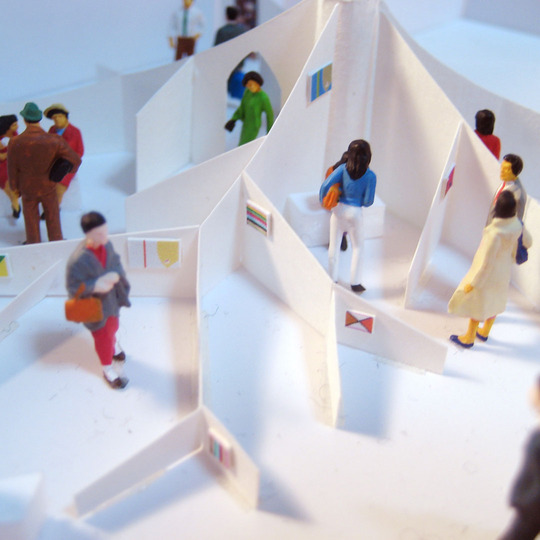
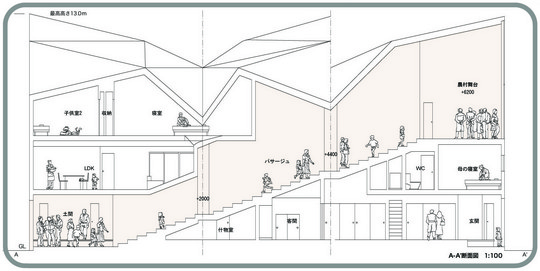
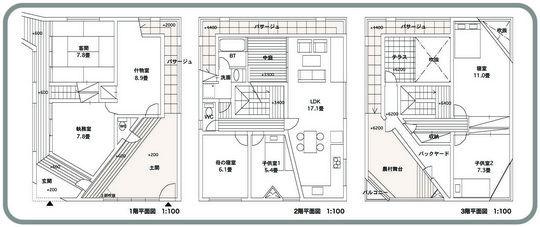
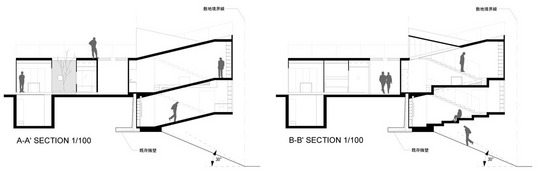
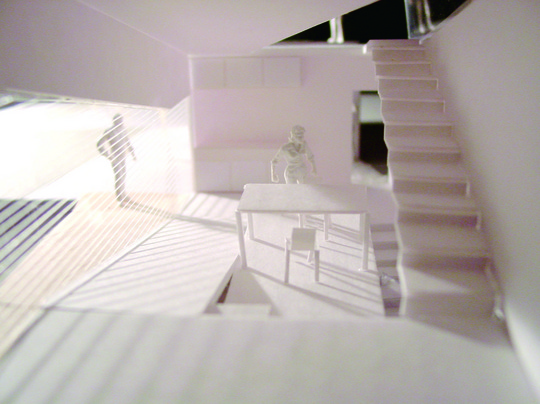
This project is a gallery for the third biggest puzzle collection in the world, and of course the biggest in Japan. Three spaces are required at the entrance hall of the existing university building: space to exhibit various collections of puzzles; space where children can freely play with puzzles; and, space to archive puzzles and documents.
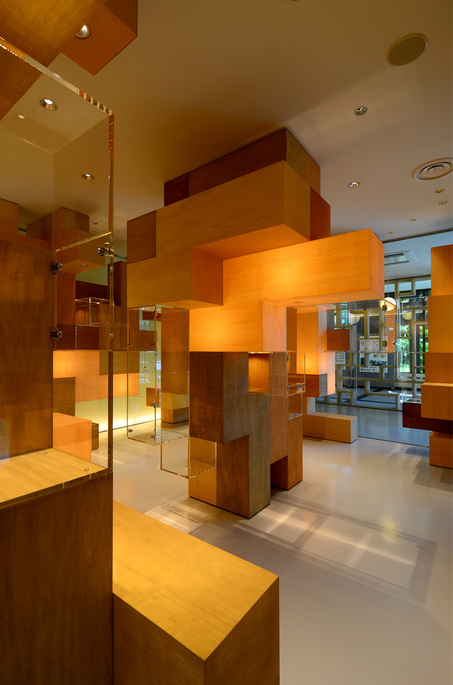
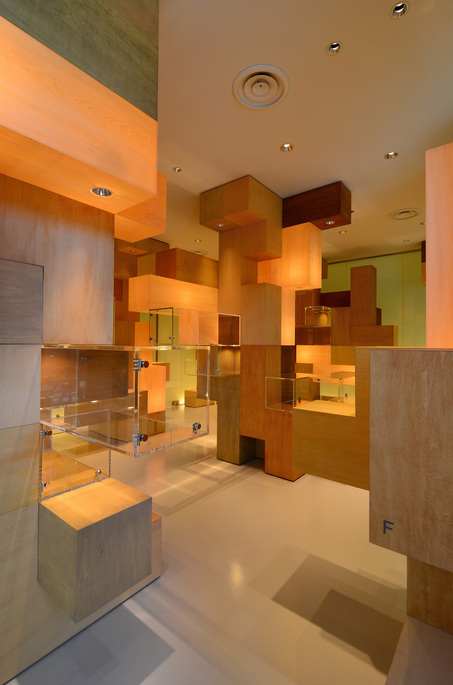
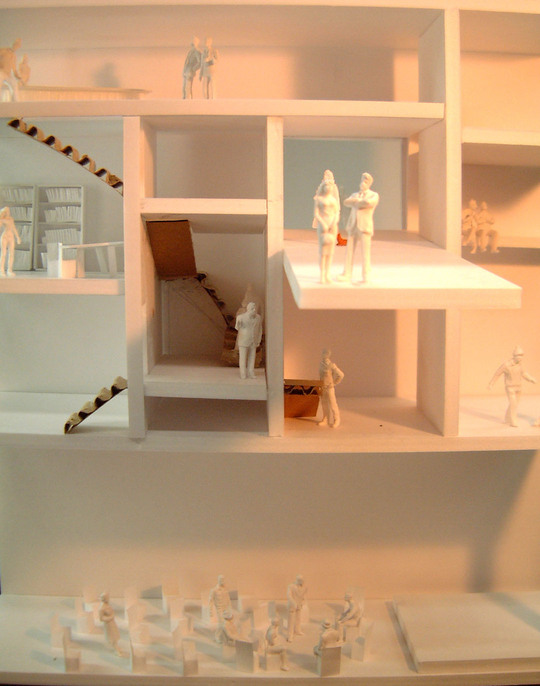
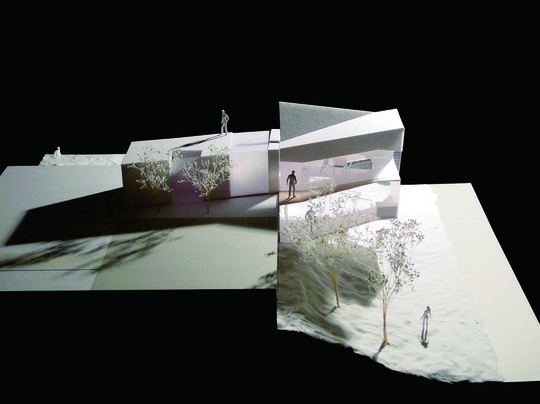
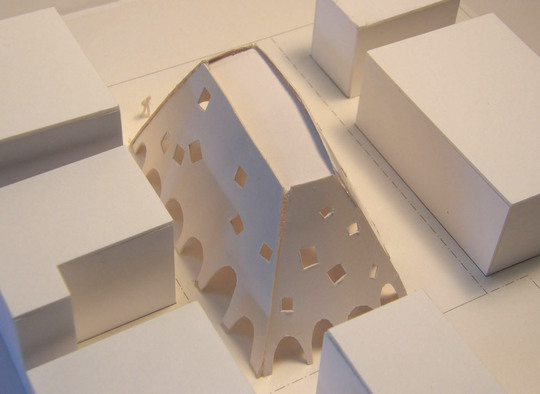
According to the scale conditions of the exhibition area and the optimum dimensions for the exhibition, we chose a cube with a side of 300 mm as the module size, and adopted an N-Pentacube, which combines five cubes as a basic unit for the space. Having assumed an 8×9×10 right-angled parallelepiped for a packing box puzzle that can be assembled into 144 N-Pentacubes, we solved this puzzle using a special algorithmic program. The completed boxed form of right-angled parallelepiped was decomposed into 12 parts, which were realigned in the gallery space.
This space is made up of identical 144 N-Pentacube form units, which invite us to imagine innumerable suppositional combinations. Visitors who enter this puzzle space will explore and solve the space Puzzle, while experiencing its special rules directly with their bodies. What we sought here are the possibilities of a space where Puzzles and Architecture coexist.
According to the scale conditions of the exhibition area and the optimum dimensions for the exhibition, we chose a cube with a side of 300 mm as the module size, and adopted an N-Pentacube, which combines five cubes as a basic unit for the space. Having assumed an 8×9×10 right-angled parallelepiped for a packing box puzzle that can be assembled into 144 N-Pentacubes, we solved this puzzle using a special algorithmic program. The completed boxed form of right-angled parallelepiped was decomposed into 12 parts, which were realigned in the gallery space.
This space is made up of identical 144 N-Pentacube form units, which invite us to imagine innumerable suppositional combinations. Visitors who enter this puzzle space will explore and solve the space Puzzle, while experiencing its special rules directly with their bodies. What we sought here are the possibilities of a space where Puzzles and Architecture coexist.